Traditional Needle Electrospinning
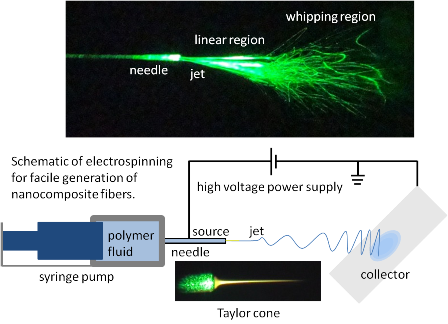
- Samples comprised of collections of nanofibers are readily fabricated, formed from a polymer-solution doped with nano-materials such as carbon nanotubes or metal nanoparticles. The dopants act to enhance the intrinsic physical properties of the polymer matrix creating a nanocomposite; such as potentially increasing the material's electrical conductance or mechanical strength. As schematically depicted below, random mats of nanofibers are produced by electrospinning a solution containing the particles and the selected polymer of interest.
- In traditional needle electrospinning (TNE), positive high voltage is applied between the conducting needle and the grounded collector. The charged solution is forced out of the confined aperture (e.g., needle) by a rate-controlled syringe pump, and then driven by the electrostatic forces, generating a Taylor cone, linear region, and whipping region. As the jet propagates, solution is removed. Ultimately, the dry nanometer-sized fibers formed are deposited in random orientations onto the collector plate where they can be utilized for subsequent mechanical or electrical measurements.
Atmospheric Surface Science
Experimental Molecular Dynamics
Polymer Nanocomposites
Research Groups
NCSU User Facilities
